-
Home > NEWS > Industry News
What is USB-C Audio and How Does It Work?
What is USB-C Audio and How Does It Work?
It’s been a few years since Apple had the guts to remove the headphone jack. While the decision was controversial, other manufacturers eventually followed suit and now most smartphones have removed the 3.5mm headphone jack.
With the 3.5mm jack gone, the only options for users are USB-C and Bluetooth. On paper, USB-C seems like a viable replacement for the headphone jack, but how does it actually work in the real world? Check out the pros and cons of USB-C Audio with Comtang USB-C Audio Manufacturer.
What is USB-C Audio?
USB Type-C is a reversible USB connector that started appearing in devices since the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) finalized its specification in 2014. Over the years, USB-C has grown in popularity and most modern smartphones, laptops, and tablets have a USB-C port. USB Type-C is designed to make life easier for users (they only have to worry about one type of cable and port) and easier for manufacturers (because they don't have to support so many different connectors).
The USB-IF released the USB Audio Device Class 3.0 specification in 2016, which aims to "establish USB Audio over USB Type-C as the premier solution for all digital audio applications, including headsets, mobile devices, docking stations, gaming setups, and VR solutions."
USB Type-C Audio was created to standardize audio output using USB Type-C. This will allow USB ports to replace 3.5mm audio jacks, and device manufacturers will be able to use one port to send and receive power, transfer file data, output video, and output audio. This will allow devices to be thinner, more durable, and potentially waterproof, according to the USB-IF.
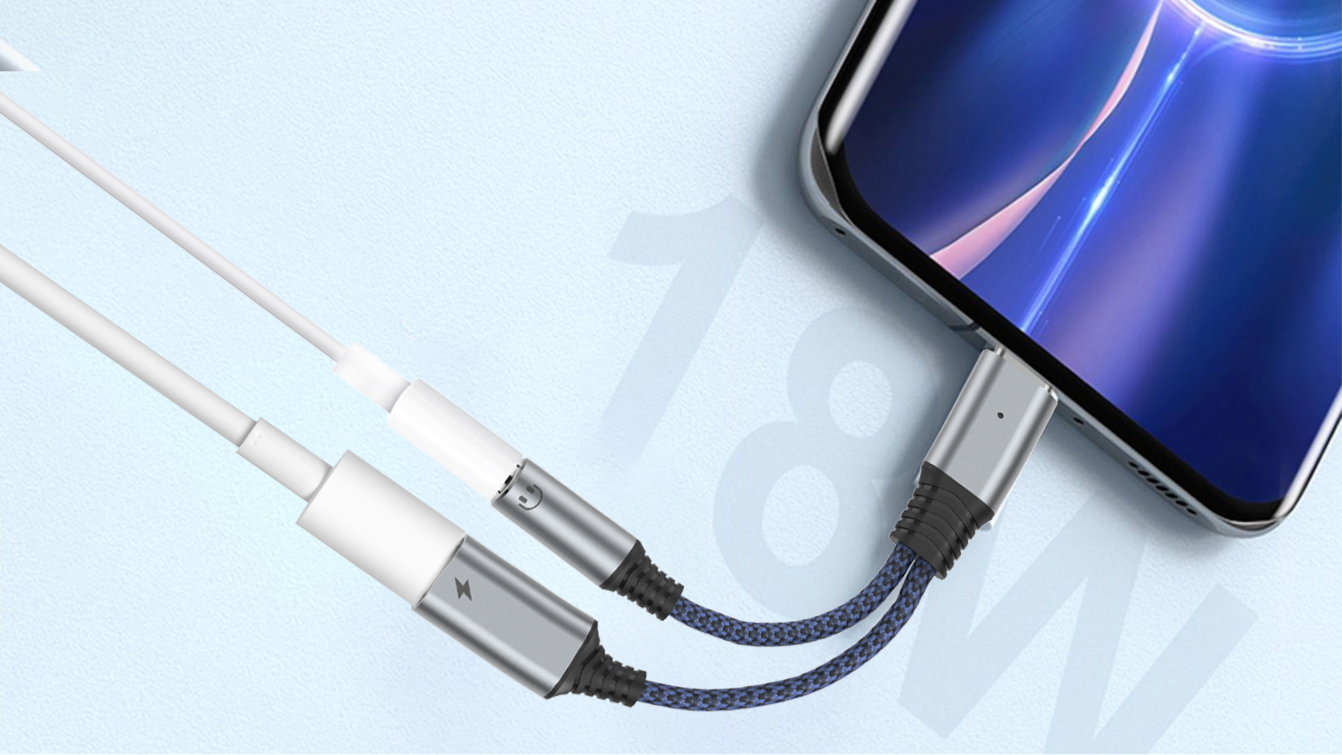
Despite serving the same purpose, USB-C Audio works differently than a headphone jack. A 3.5mm headphone jack only outputs analog audio, which is processed using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) inside a smartphone. USB Type-C will transmit digital audio, and it's up to your headphones or other listening device to convert that data and amplify the sound. USB-C can also send analog audio output like a headphone jack, as long as it's implemented in the port and your phone has a DAC for wired audio.
What are USB Audio Protocols?
Three USB-C Audio protocols (or classes) allow USB devices to act as audio peripherals. These classes apply to all types of USB connectors.
USB Audio Class 1.0 (or at least a subset of it) is natively supported by all major operating systems, including Android smartphones running 5.0 Lollipop or higher. UAC 1.0 is limited to USB 1.0 speeds (12Mbps), but supports high-resolution audio at 96kHz sampling rates. USB Audio Class 2.0 introduces faster transfer rates, supporting High-Speed USB 2.0 (480Mbps), which enables low-latency audio transmission, higher sampling rates, and more bandwidth for multiple channels. It also increases audio resolution to 32-bit/384kHz, but at the cost of higher power consumption. USB Audio Class 3.0 primarily brings improvements to power consumption and adds support for features like active noise cancellation, hotword detection, and user-defined EQ.
Audio Adapter Accessory Mode is another USB audio-related protocol. This mode allows the connector to transmit analog signals similar to a 3.5mm jack. It works by repurposing the pins on the port to accept passive audio signals. As mentioned earlier, this mode requires an internal DAC, not an external one.
Benefits of USB Type-C Audio
Since USB-C audio doesn't require a DAC in the phone, manufacturers can remove the internal DAC and free up valuable space inside the device. This also means that the DAC can now be moved to the headphones or adapter. Buyers can choose a product that delivers the sound they want, rather than being stuck with a generic and often inferior built-in DAC. Another advantage of an external DAC over an internal one is that it reduces interference caused by the power and processing hardware inside the device.
Also, by ditching the internal DAC, the phone will have to do less processing, potentially extending battery life. However, any analog headphone adapter must include a DAC, which needs to be powered by the phone.
The fact that USB Type-C can support multiple digital inputs at once means that adding an inline remote control that works across all your devices will also be much easier. It makes it possible to use hotwords like "OK Google" or "Hey Siri" through a pair of USB-C headphones. In addition, USB-C audio supports features like active noise cancellation, surround sound, and digital effects.
The Disadvantages of USB Type-C Audio
USB-C audio isn't perfect by any means, and there are several issues with this new spec.
For one, using USB-C headphones means your charging port has to double as an audio listening port, making it more susceptible to wear and tear. This also brings up the issue of charging and using wired headphones at the same time. This problem first emerged after the release of the iPhone 7, when there were some solutions that allowed you to use headphones and charge them, but they were limited to setups involving three separate cables, which was far from beautiful, clean, or convenient. You still need the same bulky setup to charge your phone and listen to music with USB Type-C headphones at the same time.
Compatibility issues are another problem with USB-C audio. You can't tell if a USB-C headset will work with your phone just by looking at it. So you might spend a lot of money on a new set of headphones only to find out that they don't work with your phone or that the volume buttons don't work. If you're going to buy USB-C headphones, get a pair with a DAC to ensure compatibility with all your devices.
What about using an adapter to connect your old analog headphones to your phone's USB-C port? In that case, you'll need an adapter that includes a DAC, and the quality of these adapters tends to vary widely. A lower-quality adapter will be cheap, while a decent adapter might cost you as much as another pair of headphones.
For decades, the 3.5mm jack was the mainstream because it was simple. There was no charging or extra cables. You just picked up the headphones, plugged them in, and listened. Simplicity was the key to its success. USB Type-C audio complicated that process, ultimately prompting a shift to wireless headphones.
USB Type-C Headphones vs. Bluetooth Headphones
Besides the analog jack, the main competitor to USB Type-C audio is Bluetooth. Released in July 2016, Bluetooth 5.0 quadruples the operating range, doubles the speed, and increases the data broadcasting capabilities of Low Energy (LE) devices eightfold. This makes it a worthy replacement for the abandoned 3.5mm jack, but it is not without its limitations.
In general, Bluetooth headphones do not sound as good as similarly priced wired headphones. They are also less durable and less reliable. However, the pros still outweigh the cons, and anyone who is not a strict audiophile will get a good pair of Bluetooth headphones.
You can find more details in our comparison of USB, standard (3.5mm), and Bluetooth headphones.
USB-C Audio Is Not the Best 3.5mm Jack Replacement
While the technology has many benefits, USB Type-C audio is far from the 3.5mm headphone jack replacement it was advertised to be. Compatibility issues, a lack of substantial improvements to the 3.5mm jack, and improvements to wireless audio over the years have led to very low adoption rates by users and manufacturers.
However, it doesn't look like the headphone jack will be returning to smartphones anytime soon, so for better or worse, we're stuck with USB-C audio. Hopefully, future upgrades to USB-C audio bring much-needed improvements, and we get cheaper, better headphones/adapters in this category.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)